- Home
- Glossary Term
- Field Service Management
Introduction
Field Service Management (FSM) represents a critical business discipline that enables organizations to coordinate, optimize, and deliver services outside their primary facilities. As businesses increasingly rely on mobile workforces and on-site service delivery, understanding FSM has become essential for operational success and competitive advantage.

What is Field Services Management?
Field Service Management is the comprehensive coordination of a company’s resources, including employees, equipment, and operations, to deliver services at customer locations rather than at company premises. This multifaceted approach encompasses everything from initial service requests through final invoicing, creating an integrated system that maximizes efficiency while ensuring exceptional customer experiences.
At its core, FSM involves managing workers who perform tasks outside the traditional office environment. These field workers include technicians, engineers, healthcare professionals, sales representatives, and various specialists who deliver services directly to customers at their locations. The scope of field service has expanded dramatically, with approximately 80% of the global workforce now classified as “deskless,” working in environments that require mobility and flexibility.
Core Components of Field Service Management
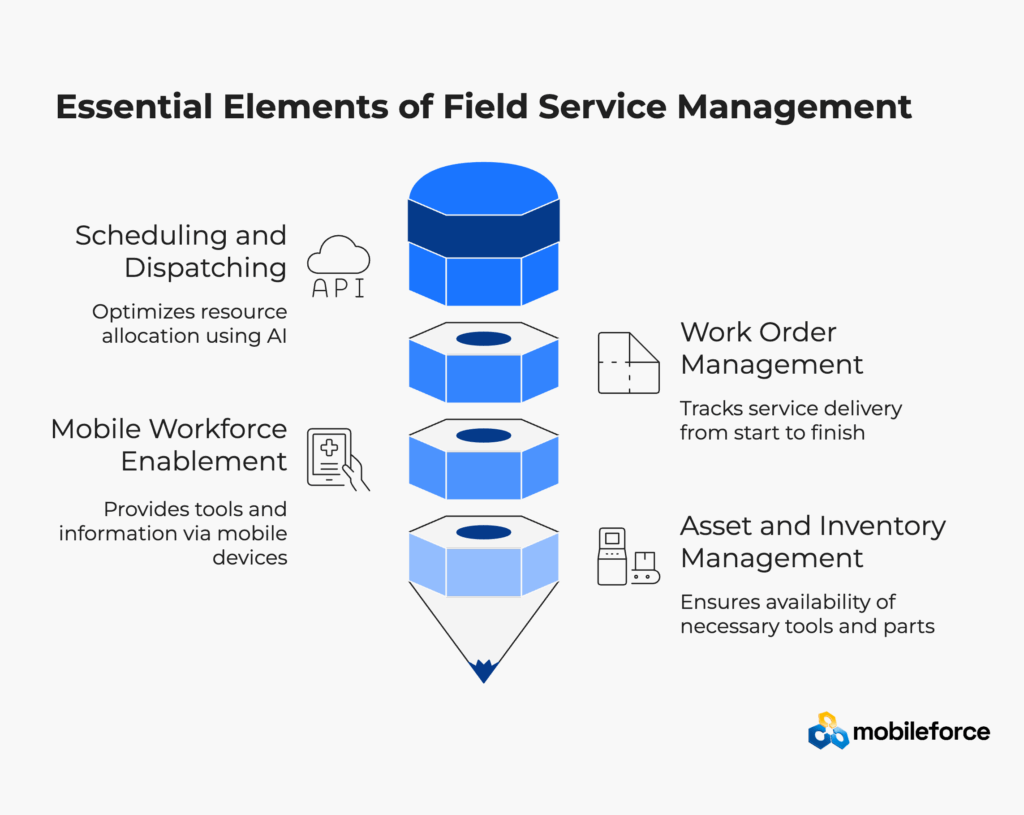
Scheduling and Dispatching
The foundation of effective FSM lies in intelligent scheduling and dispatching systems that optimize resource allocation. Modern FSM platforms use advanced algorithms to match technicians with appropriate jobs based on multiple factors including skill sets, geographic proximity, availability, and workload capacity. Smart scheduling tools leverage artificial intelligence to create dynamic schedules that automatically adjust to real-time conditions, ensuring optimal resource utilization throughout the day.
Work Order Management
Work order management serves as the central nervous system of field service operations, tracking every aspect of service delivery from initial request through completion. This component involves creating detailed work orders that include comprehensive job information, customer history, required tools and materials, safety instructions, and performance standards. Modern work order systems provide real-time visibility into job progress, enabling managers to monitor completion status and make necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
Mobile Workforce Enablement
Mobile technology represents a transformative element in modern FSM, providing field technicians with comprehensive tools and information access through smartphones and tablets. Mobile FSM applications enable technicians to view schedules, access customer information, update work orders, capture digital signatures, process payments, and communicate with headquarters in real-time. This connectivity ensures that field workers have the resources necessary to resolve issues effectively on the first visit.
Asset and Inventory Management
Comprehensive asset and inventory management ensures that technicians have access to the correct tools, parts, and equipment required for each job. Advanced FSM systems provide real-time inventory visibility, automated reordering capabilities, and predictive analytics to anticipate parts requirements based on service patterns and equipment maintenance schedules.
Key Benefits of Field Service Management
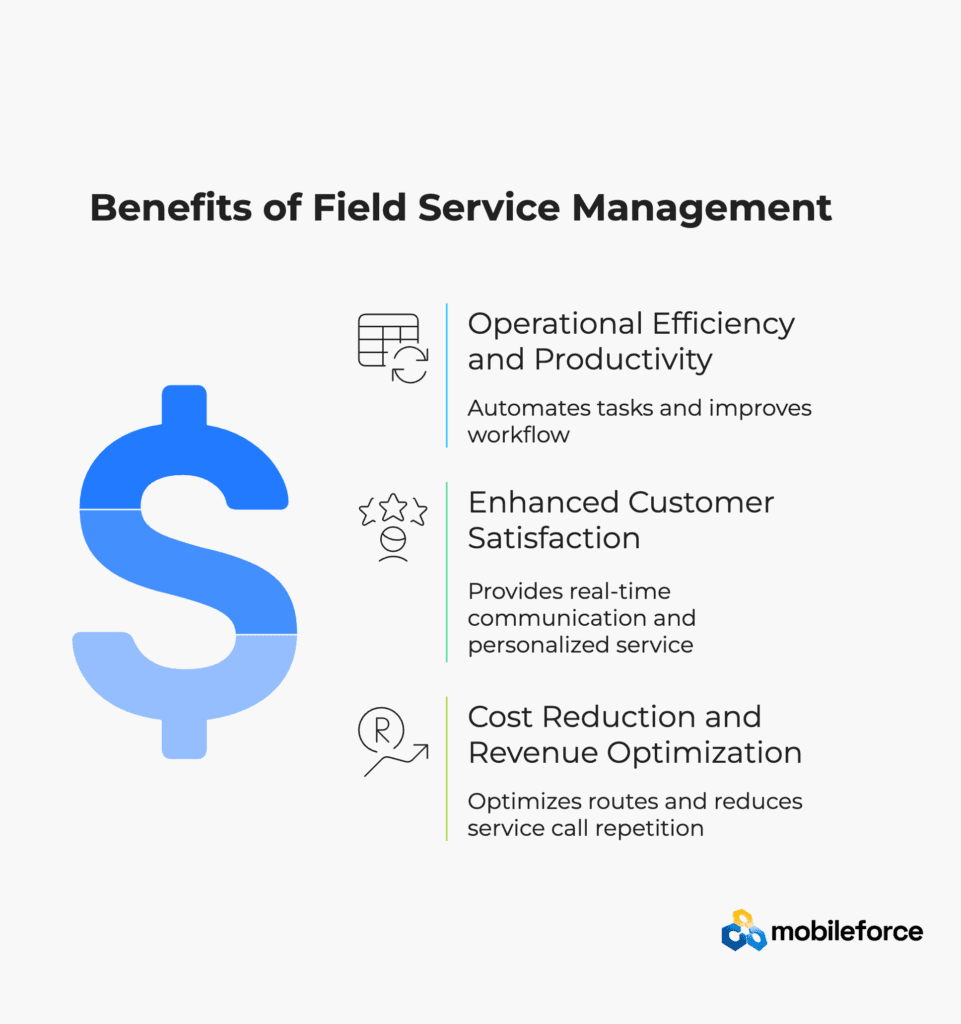
Operational Efficiency and Productivity
FSM software significantly enhances operational efficiency by automating routine tasks and eliminating manual processes that consume valuable time and resources. Studies indicate that organizations implementing AI-driven FSM systems experience improved field service efficiency and increased organizational agility. Automation of workflow processes ensures consistent service delivery while reducing the potential for human error in scheduling and resource allocation.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction improvements represent one of the most significant benefits of modern FSM implementation. Real-time communication, accurate scheduling, and first-time fix capabilities create positive customer experiences that drive loyalty and repeat business. FSM platforms enable businesses to provide personalized service experiences by maintaining comprehensive customer histories, preferences, and service records.
Cost Reduction and Revenue Optimization
Effective FSM implementation drives significant cost reductions through optimized routing, improved resource utilization, and reduced service call repetition. Route optimization minimizes fuel costs and travel time, while improved first-time fix rates eliminate costly return visits and additional labor expenses. Revenue optimization occurs through enhanced service capacity, improved billing accuracy, and expanded service opportunities.
Common Field Service Management Challenges
Scheduling and Resource Optimization
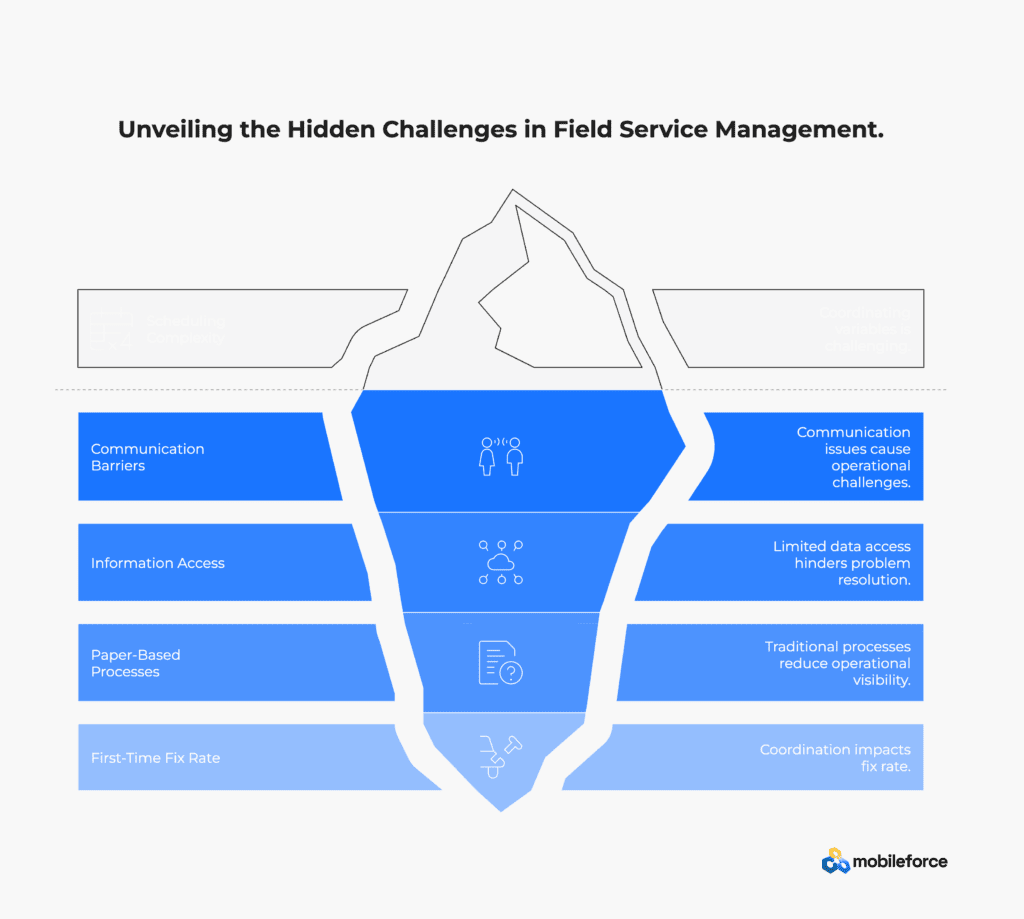
Scheduling complexity represents one of the most persistent challenges in field service management, involving the coordination of multiple variables including technician availability, skill requirements, customer preferences, and geographic constraints. Emergency service requests and last-minute cancellations can disrupt carefully planned schedules, creating inefficiencies and customer dissatisfaction.
Communication and Information Access
Communication barriers between field technicians, dispatchers, and customers create significant operational challenges. Limited real-time data access in the field can hinder effective problem resolution, while poor communication channels lead to delays and customer frustration. Traditional paper-based processes exacerbate these challenges by creating information silos and reducing operational visibility.
First-Time Fix Rate Optimization
Achieving high first-time fix rates requires precise coordination of technician skills, parts availability, and diagnostic accuracy. Poor first-time fix rates result in costly return visits, reduced customer satisfaction, and decreased operational efficiency. Factors affecting first-time fix rates include inadequate job preparation, insufficient parts inventory, skill mismatches, and limited access to expert support during complex repairs.
Technology Integration and Digital Transformation
Internet of Things (IoT) and Predictive Maintenance
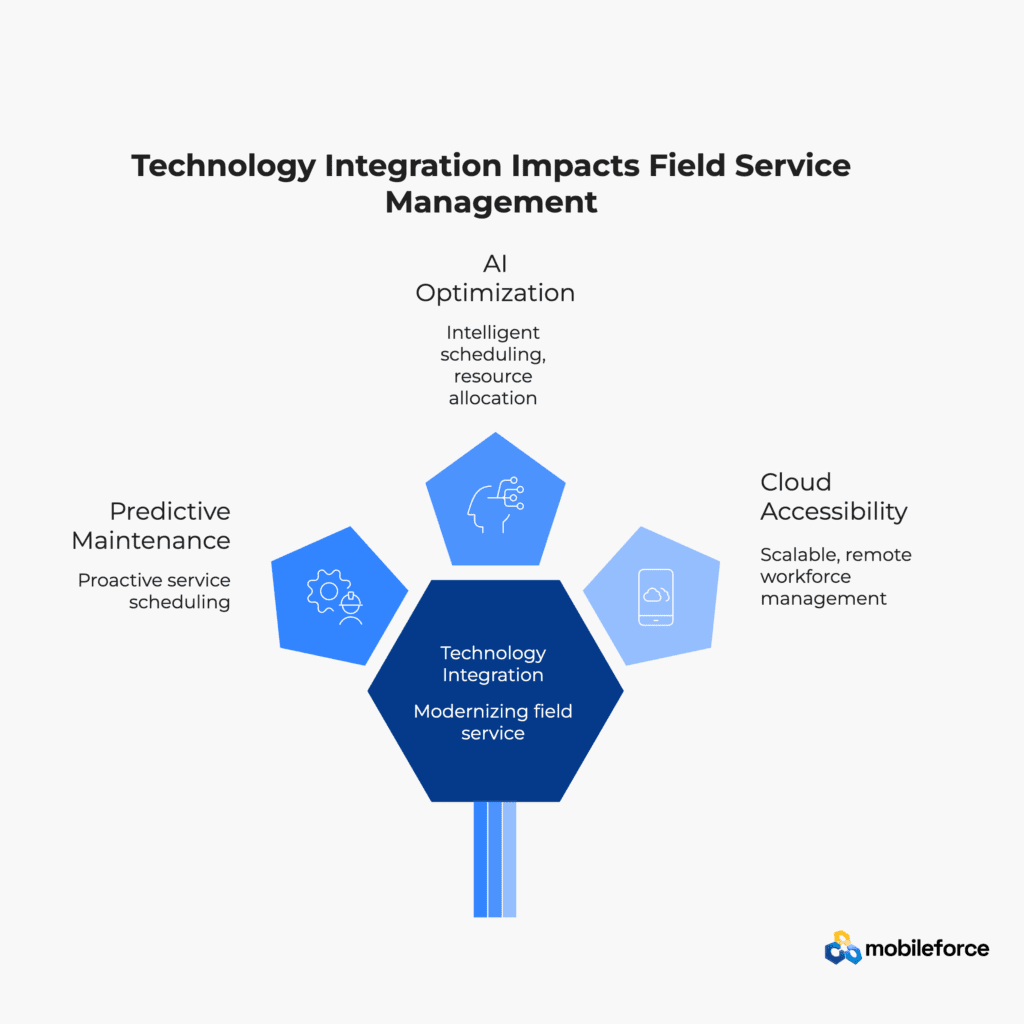
IoT integration represents a transformative capability in modern FSM, enabling real-time equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance strategies. Connected devices provide continuous performance data that helps identify potential failures before they occur, enabling proactive service scheduling and reducing unexpected downtime. Predictive maintenance capabilities use machine learning algorithms to analyze equipment performance patterns and predict optimal maintenance intervals.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-powered FSM systems provide intelligent scheduling optimization, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making capabilities that enhance operational efficiency. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical service data to identify patterns, optimize resource allocation, and improve service delivery processes. AI capabilities include intelligent route optimization, automated scheduling recommendations, and predictive parts ordering that reduces inventory costs while ensuring parts availability.
Cloud-Based Platforms and Mobile Integration
Cloud-based FSM platforms provide scalable, accessible solutions that support remote workforce management and real-time collaboration. Cloud deployment eliminates infrastructure requirements while providing automatic updates and enhanced security capabilities. Mobile integration ensures that field technicians have constant access to critical information and communication tools regardless of location or connectivity status.
Industry Applications
Field Service Management (FSM) is widely adopted across industries where operational efficiency, compliance, and timely service delivery are mission-critical. Each sector has unique demands that shape how FSM solutions are implemented, integrating specialized workflows, regulatory adherence, and asset-intensive operations.
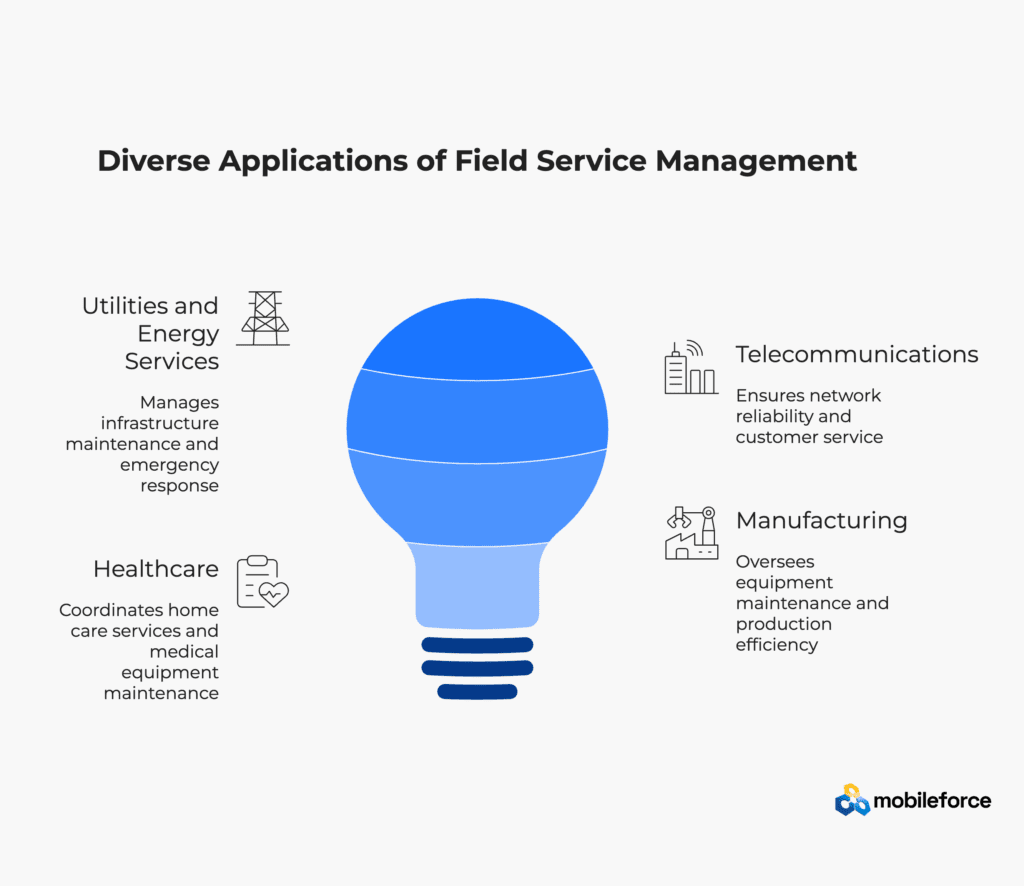
Utilities and Energy Services
In utilities and energy, FSM plays a central role in maintaining extensive infrastructure networks, managing outages, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Energy providers use FSM to schedule preventive maintenance, track field assets, and respond to emergencies such as grid failures or gas leaks. With real-time monitoring and mobile workforce management, technicians can quickly access site data, adhere to safety protocols, and restore services efficiently. Integration with IoT devices enables predictive maintenance of transformers, pipelines, and smart meters, reducing downtime and operational risk.
Telecommunications
Telecom companies rely on FSM to manage high volumes of installation, repair, and network maintenance tasks. FSM systems optimize technician dispatching based on skill sets and location, ensuring fast service delivery and minimizing customer disruptions. With growing demand for fiber optics, 5G rollouts, and network upgrades, FSM supports project tracking, inventory management, and compliance with service level agreements (SLAs). Remote diagnostic tools and augmented reality further improve first-time fix rates and reduce truck rolls.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
In healthcare, FSM ensures timely and compliant delivery of patient-centered services such as home healthcare visits, medical equipment maintenance, and laboratory logistics. Mobile-enabled FSM solutions give care providers secure access to patient records, route optimization tools, and compliance checklists to meet stringent health and safety standards. Equipment manufacturers and biomedical service firms use FSM to manage the maintenance of diagnostic devices, imaging systems, and life-support machinery, where downtime can directly impact patient outcomes.
Manufacturing and Industrial Services
Manufacturers and industrial service providers use FSM to maintain production equipment, support warranty repairs, and manage service contracts for industrial machinery. Predictive maintenance powered by IoT sensors allows teams to detect potential failures early, reducing unplanned downtime and costly disruptions in production lines. FSM platforms also help track spare parts inventory, schedule skilled technicians, and document service history for compliance audits and customer reporting.
Construction and Infrastructure
Construction companies employ FSM to manage heavy equipment maintenance, site inspections, and contractor scheduling. The ability to track machinery performance, ensure safety certifications, and dispatch specialized crews enhances project efficiency and compliance with labor and safety regulations.
Oil and Gas
In oil and gas, FSM supports the coordination of remote field teams working on pipelines, drilling rigs, and refineries. Harsh environments and strict regulatory oversight demand robust FSM systems capable of real-time communication, safety monitoring, and asset tracking to reduce operational risks and ensure worker safety.
Implementation Best Practices
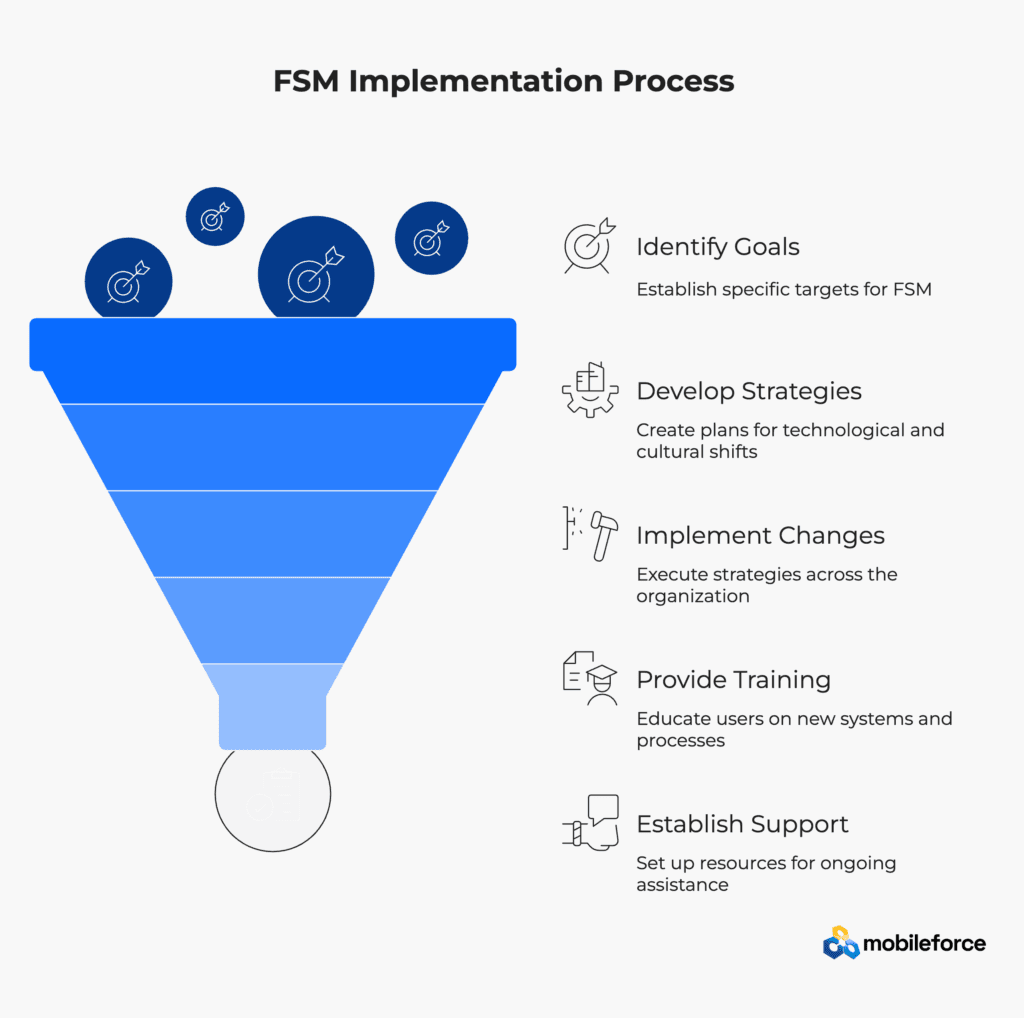
Successful FSM implementation begins with clear identification of business objectives and desired outcomes. Organizations must define specific goals including efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and customer satisfaction targets to guide implementation decisions. Comprehensive change management strategies address both technological and cultural shifts required for successful FSM adoption, including training programs for all user groups and establishing support resources.
Conclusion
Field Service Management represents a fundamental transformation in how organizations deliver services and manage mobile workforces. By integrating advanced technologies with strategic operational practices, FSM enables businesses to achieve operational excellence while delivering exceptional customer experiences. As digital transformation continues to reshape service industries, FSM will remain essential for organizations seeking competitive advantage through superior service delivery and operational efficiency.