- Home
- Glossary Term
- Sales Operations
Introduction
Sales Operations (commonly referred to as “Sales Ops”) is a strategic business function that optimizes sales processes, manages sales technology infrastructure, and provides analytical support to enable sales teams to operate more efficiently and effectively. Sales Operations serves as the operational backbone of the sales organization, focusing on process improvement, data management, strategic planning, and technology implementation to drive revenue growth and sales productivity.
At its core, Sales Operations reduces friction in the sales process by handling all non-selling administrative tasks, allowing sales representatives to focus their time and energy on customer-facing activities and closing deals. The function encompasses everything from sales process design and territory planning to compensation management and performance analytics.
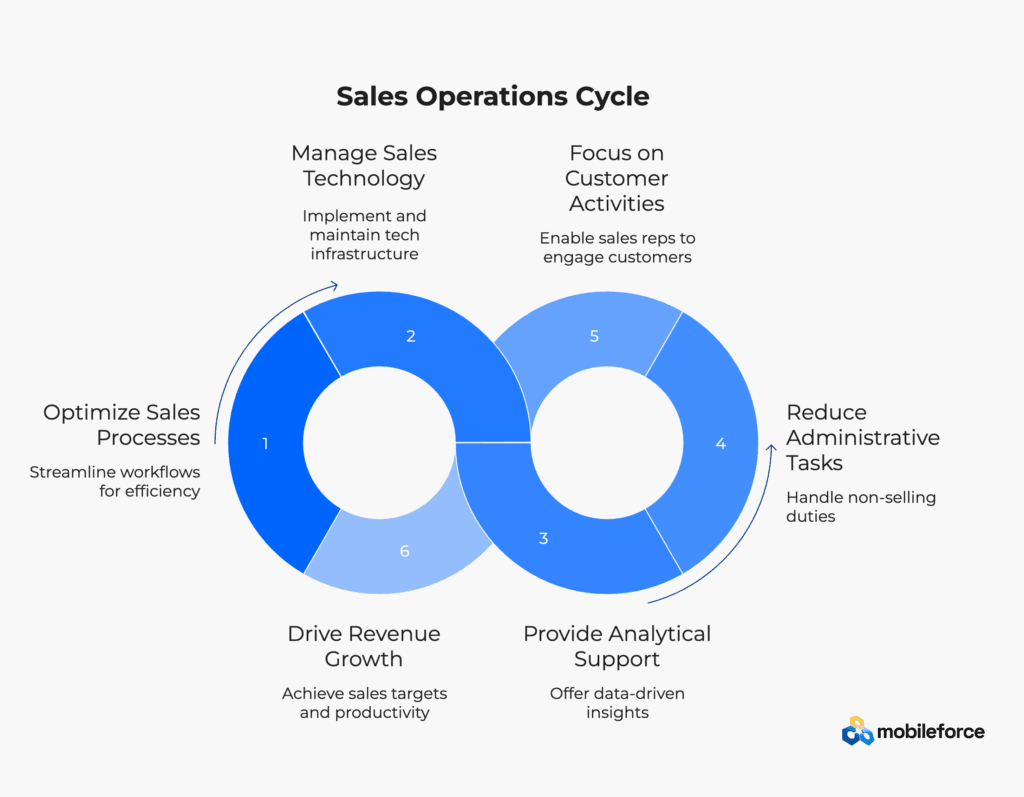
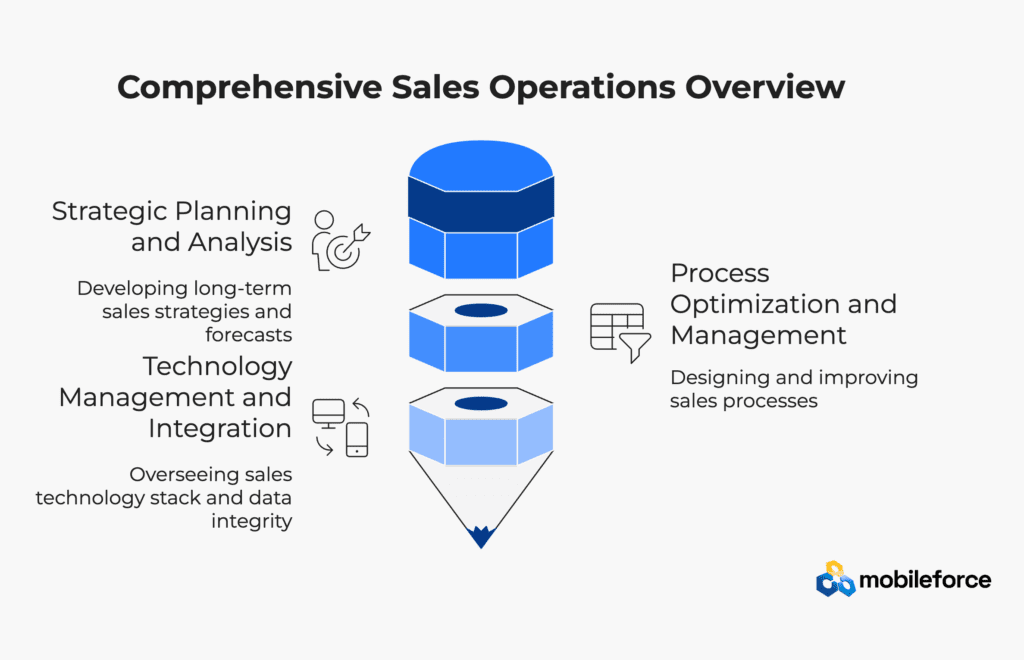
Core Functions and Responsibilities
Strategic Planning and Analysis
Sales Operations teams are responsible for developing long-term sales strategies aligned with business objectives. This includes territory planning to ensure optimal coverage and resource allocation, capacity planning to determine staffing needs, quota planning to set realistic yet challenging targets, and compensation planning to design incentive structures that drive desired behaviors and outcomes.
The strategic role extends to sales forecasting, where teams analyze historical data, market trends, and pipeline health to provide accurate revenue predictions. These forecasts are crucial for business planning, resource allocation, and investor communications.
Process Optimization and Management
One of the primary responsibilities of Sales Operations is to design, implement, and continuously improve sales processes. This involves mapping out the entire customer journey from lead generation through deal closure, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and implementing solutions to streamline workflows.
Process optimization includes establishing standardized methodologies for prospecting, qualification, demonstration, negotiation, and closing. Sales Operations teams also manage the handoff processes between marketing and sales, ensuring that leads are properly qualified and transferred without information loss.
Technology Management and Integration
Sales Operations oversees the entire sales technology stack, including Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, sales enablement platforms, Configure Price Quote (CPQ) tools, sales analytics software, and various automation platforms. This responsibility includes vendor selection, implementation, integration, maintenance, and user training.
The team ensures that all sales technologies work together seamlessly, providing sales representatives with a unified view of customer information and enabling automated workflows that reduce manual tasks. They also manage data integrity, ensuring that customer information is accurate, complete, and consistently formatted across all systems.
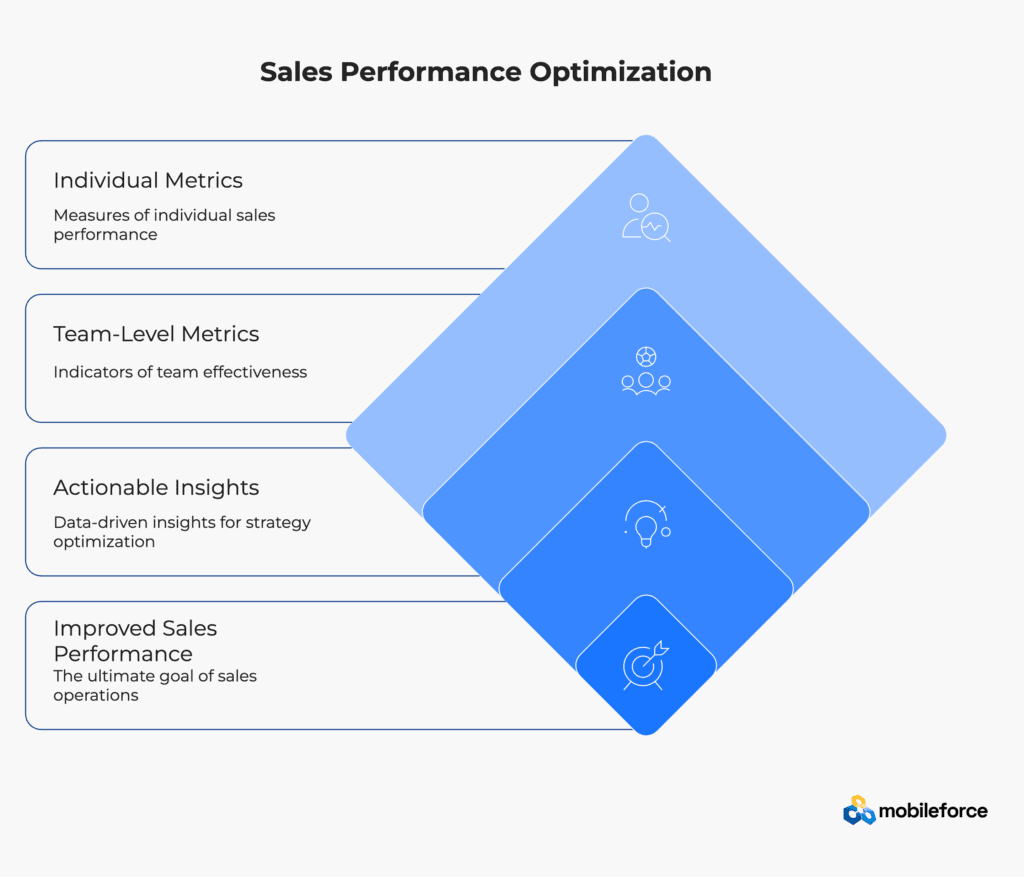
Performance Measurement and Analytics
Sales Operations teams are responsible for defining, tracking, and analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure sales effectiveness. This includes both individual performance metrics such as quota attainment, activity levels, and conversion rates, as well as team-level metrics like pipeline velocity, deal size trends, and revenue predictability.
Advanced analytics capabilities enable Sales Operations to identify patterns in successful deals, understand which activities drive the best outcomes, and provide actionable insights to both individual representatives and sales leadership. This data-driven approach helps optimize sales strategies and improve overall performance.
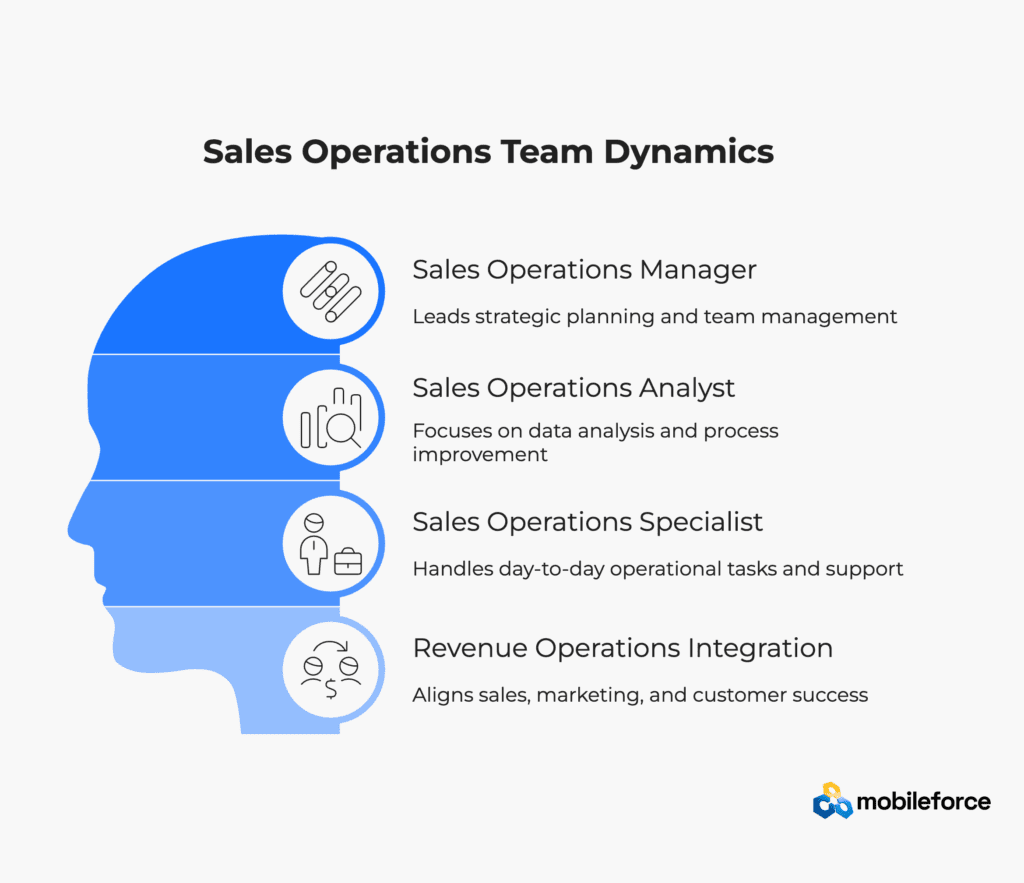
Team Structure and Roles
Sales Operations Manager
The Sales Operations Manager serves as the strategic leader of the function, partnering with sales leadership to develop and execute operational strategies. They are responsible for translating executive vision into actionable plans, managing the sales operations team, and ensuring alignment between sales activities and business objectives.
Sales Operations Analyst
Sales Operations Analysts focus on data analysis, reporting, and process improvement. They spend their time analyzing sales performance data, creating reports and dashboards, conducting research on market trends and competitive intelligence, and identifying opportunities for optimization.
Sales Operations Specialist
Sales Operations Specialists handle day-to-day operational tasks such as CRM administration, lead management, sales tool training, and process documentation. They serve as the primary point of contact for sales representatives who need technical support or process clarification.
Revenue Operations Integration
In many organizations, Sales Operations is evolving toward or integrating with Revenue Operations (RevOps), a broader function that aligns sales, marketing, and customer success operations. This evolution reflects the need for greater coordination across all revenue-generating functions to create a seamless customer experience and optimize the entire revenue cycle.
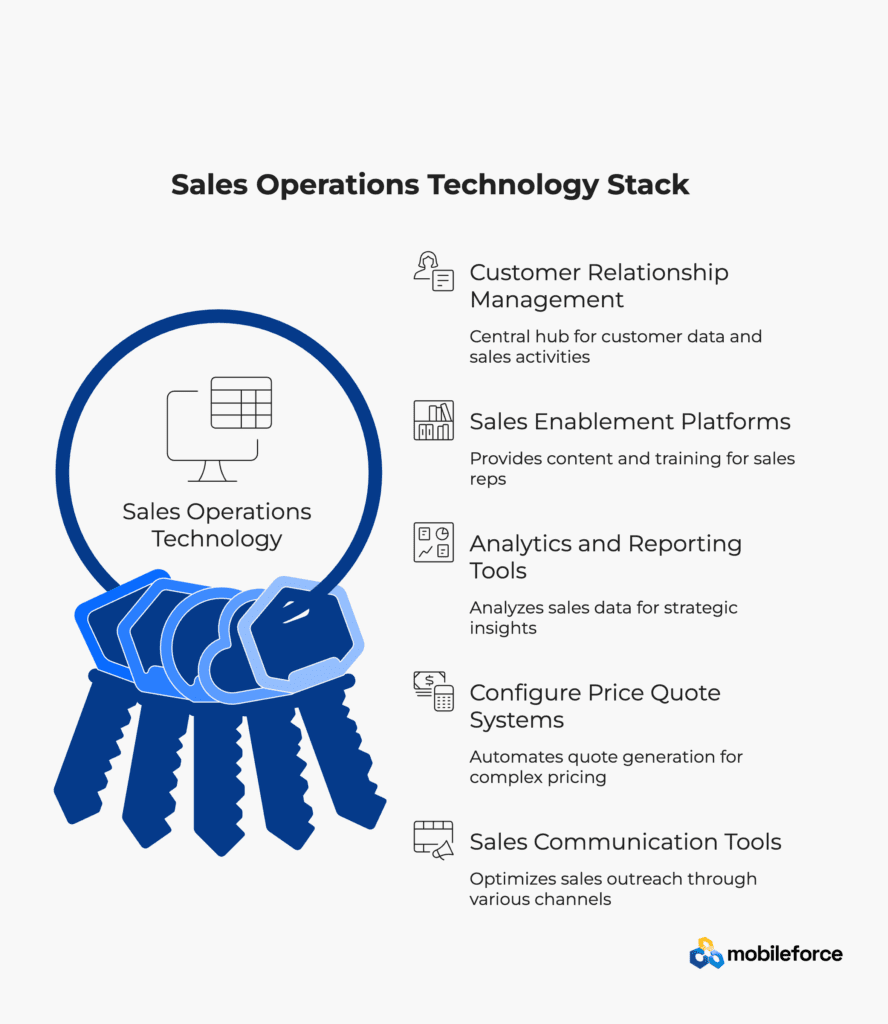
Technology Stack and Tools
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM system serves as the central hub for all customer information and sales activities. Sales Operations teams are responsible for CRM configuration, data management, user permissions, and integration with other business systems. Popular platforms include Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics, and Pipedrive.
Sales Enablement Platforms
These tools provide sales representatives with the content, training, and resources they need to engage effectively with prospects and customers. Sales Operations manages content libraries, tracks usage analytics, and ensures that materials are current and aligned with messaging strategies.
Analytics and Reporting Tools
Business intelligence platforms enable Sales Operations to analyze sales data, create custom reports, and build interactive dashboards. These tools help identify trends, measure performance against targets, and provide insights for strategic decision-making.
Configure Price Quote (CPQ) Systems
For organizations with complex products or pricing structures, CPQ systems automate the quote generation process, ensuring accuracy and reducing cycle time. Sales Operations manages product catalogs, pricing rules, approval workflows, and integration with other systems.
Sales Communication and Engagement Tools
These platforms help automate and optimize sales outreach through email sequences, social selling, and multi-channel communication campaigns. Sales Operations evaluates tools, manages integrations, and tracks effectiveness.
Key Performance Indicators and Metrics
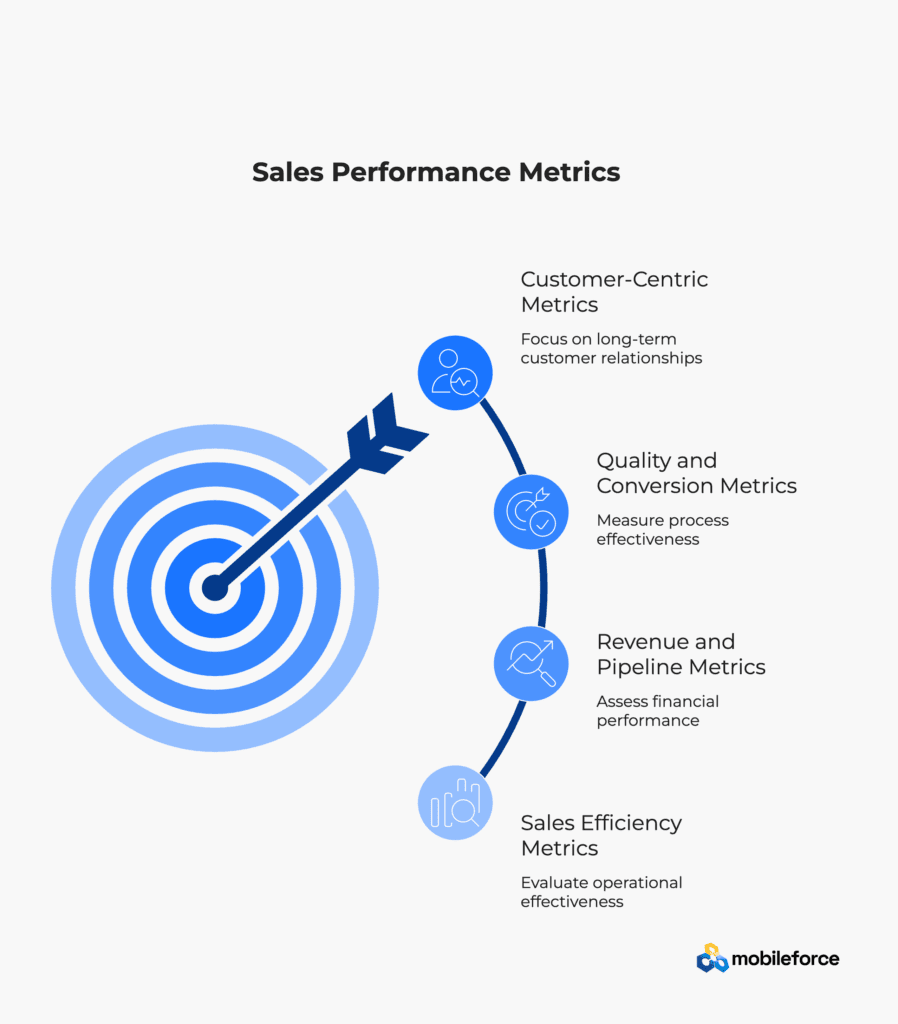
Sales Efficiency Metrics
Sales Operations tracks various efficiency metrics to understand how effectively the sales team is operating. These include sales cycle length, which measures the average time from initial contact to deal closure; win rates, which indicate the percentage of opportunities that result in closed deals; and activity metrics such as calls made, emails sent, and meetings scheduled.
Revenue and Pipeline Metrics
Revenue-focused metrics include total sales revenue, revenue growth rates, average deal size, and pipeline coverage ratios. These metrics help assess whether the sales team is on track to meet targets and identify potential shortfalls early enough to take corrective action.
Quality and Conversion Metrics
These metrics measure the quality of sales activities and the effectiveness of the sales process. Examples include lead-to-opportunity conversion rates, opportunity-to-close ratios, and the percentage of deals that meet target margins. These metrics help identify areas where process improvements can have the greatest impact.
Customer-Centric Metrics
Modern Sales Operations also tracks metrics related to customer satisfaction and lifetime value, recognizing that sales success extends beyond the initial transaction. This includes customer retention rates, expansion revenue, and customer satisfaction scores.
Best Practices and Strategic Considerations
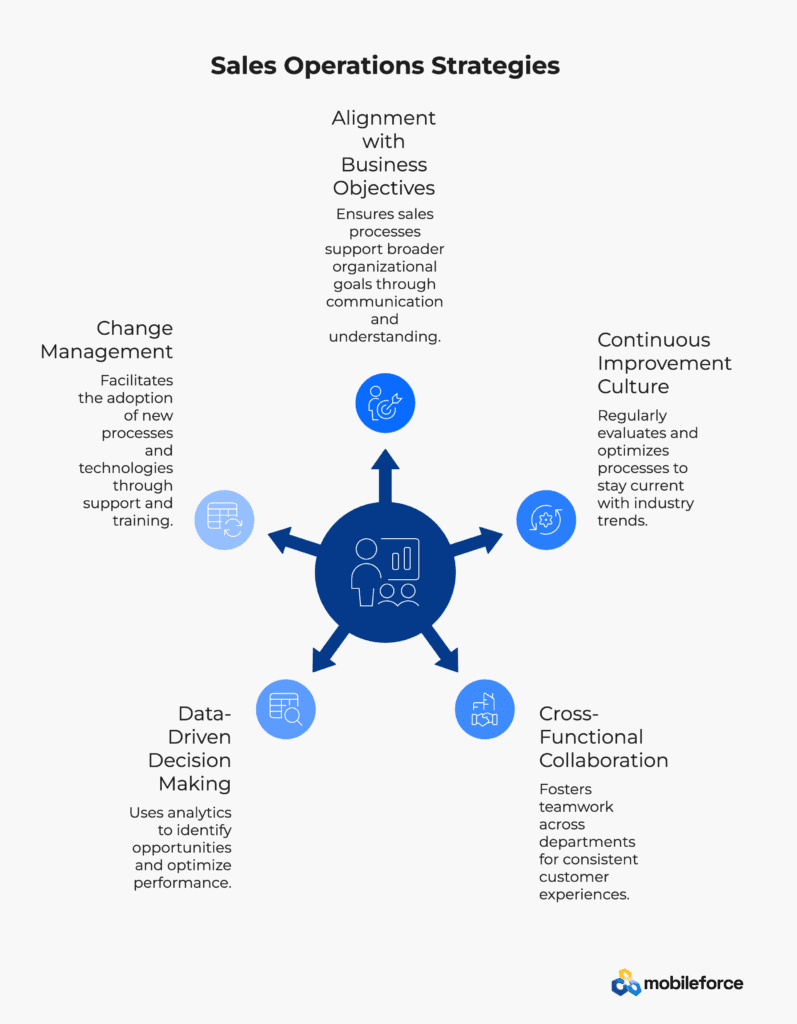
Alignment with Business Objectives
Successful Sales Operations functions maintain close alignment with overall business strategy, ensuring that sales processes and metrics support broader organizational goals. This requires regular communication with executive leadership and other departments to understand strategic priorities and market dynamics.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Leading Sales Operations teams embrace a culture of continuous improvement, regularly evaluating processes, analyzing performance data, and implementing optimizations. This includes staying current with industry best practices, emerging technologies, and evolving customer expectations.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Effective Sales Operations requires strong collaboration with marketing, customer success, finance, and other departments. This collaboration ensures consistent customer experiences, efficient lead handoffs, and aligned measurement frameworks across the revenue organization.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The most successful Sales Operations teams base their decisions on data rather than intuition, using analytics to identify opportunities, measure the impact of changes, and optimize performance. This requires investing in quality data management practices and analytical capabilities.
Change Management
As Sales Operations implements new processes and technologies, effective change management becomes critical. This includes clear communication, comprehensive training, and ongoing support to ensure that sales teams adopt new approaches and realize the intended benefits.
Conclusion
Sales Operations has grown from an administrative support role into a strategic engine that drives sales productivity, efficiency, and predictable revenue growth. By optimizing processes, managing technology, and leveraging data-driven insights, Sales Ops enables sales teams to focus on selling while ensuring alignment with broader business goals. As the function evolves toward integrated Revenue Operations and adopts advanced analytics and automation, organizations that invest in strong Sales Operations capabilities will be best positioned to scale, delight customers, and achieve sustained competitive advantage.