- Home
- Glossary Term
- Asset Lifecycle Management
What is Asset Lifecycle Management?
Asset Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a comprehensive framework that optimizes the value, performance, and cost-effectiveness of physical and digital assets throughout their entire operational lifespan. This strategic approach encompasses planning, acquisition, deployment, operation, maintenance, and disposal of assets to maximize return on investment while minimizing total cost of ownership.
ALM integrates seamlessly with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for financial tracking and procurement workflows, while connecting with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) for operational maintenance execution. Modern implementations leverage Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and predictive analytics to transform reactive asset management into proactive, data-driven optimization strategies.
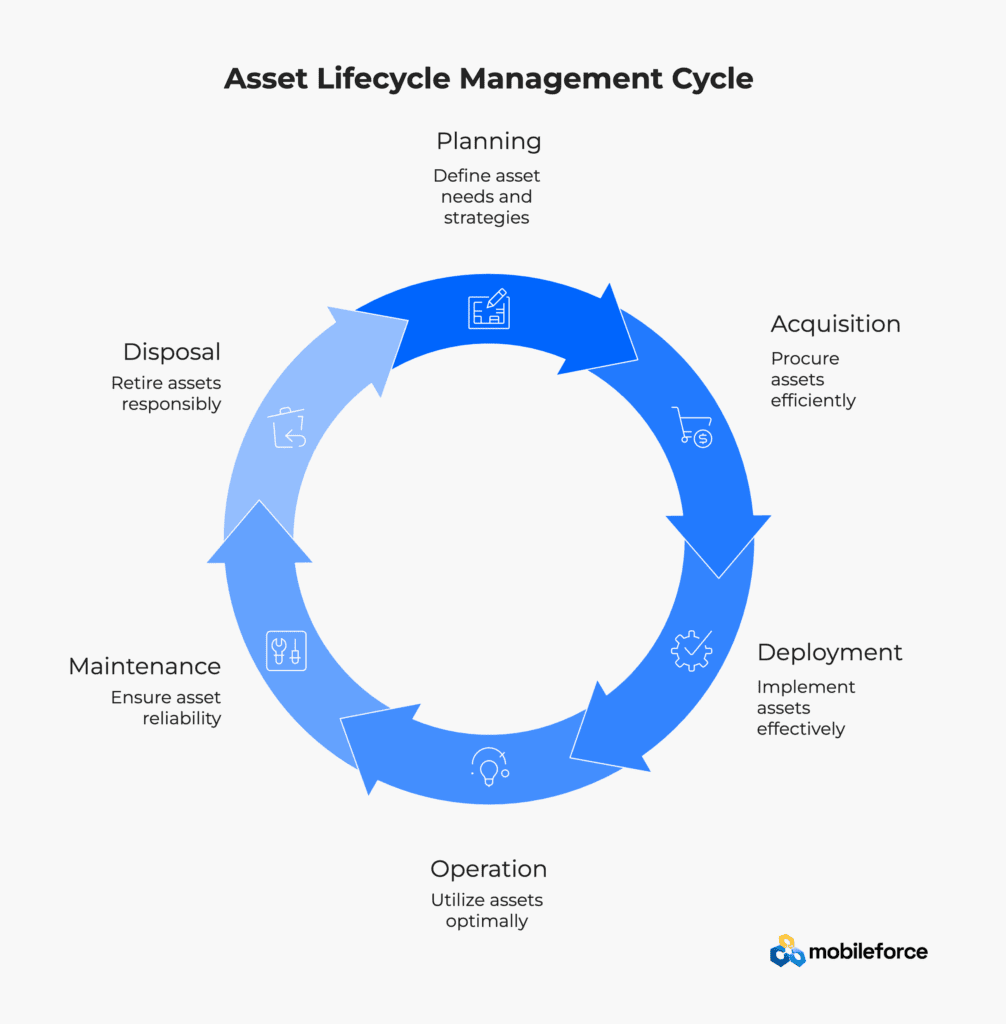
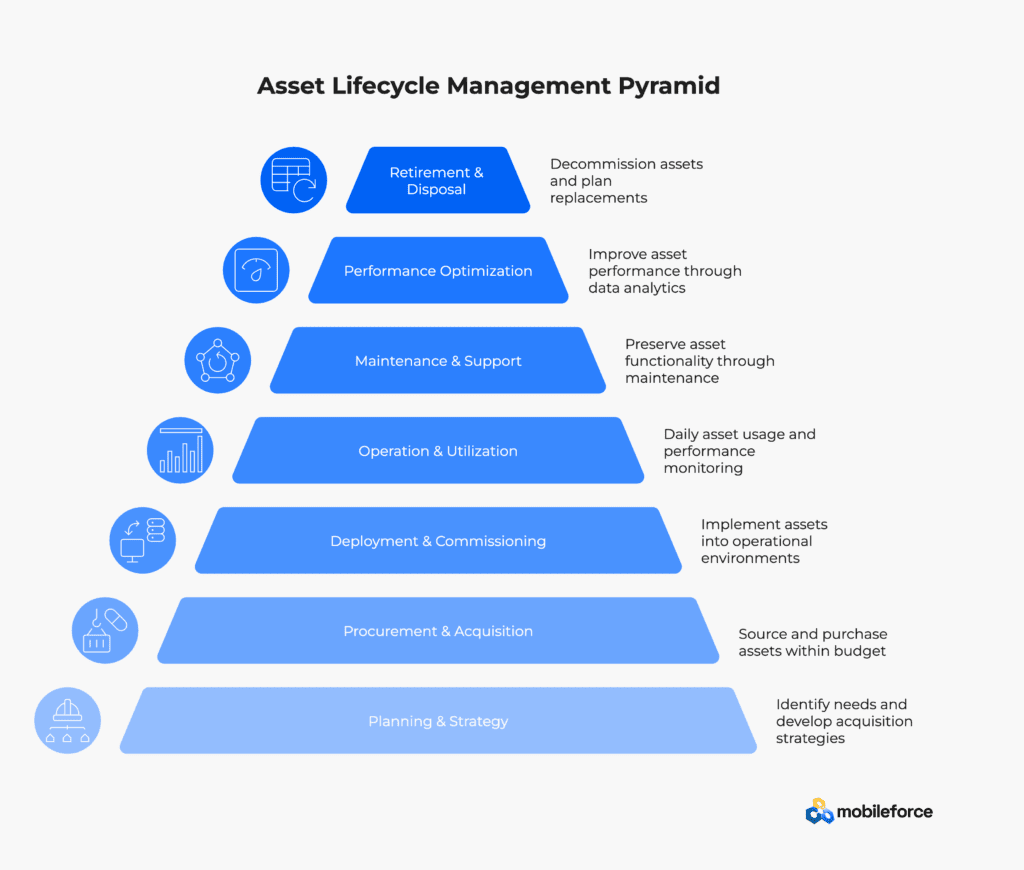
The Seven Phases of Asset Lifecycle Management
Asset Planning and Strategy
The foundational phase where organizations identify asset requirements, evaluate alternatives, and develop acquisition strategies aligned with business objectives. Activities include needs assessment, technology evaluation, financial modeling, and risk analysis. This phase establishes specifications that guide procurement processes and inform ERP system configurations.
Asset Procurement and Acquisition
The systematic process of sourcing, evaluating, and purchasing assets based on established criteria and budgetary constraints. Includes vendor selection, contract negotiation, quality assurance, and delivery coordination. Procurement data integrates with ERP systems for financial tracking and CMMS platforms for asset registration.
Asset Deployment and Commissioning
The controlled implementation of assets into operational environments, encompassing installation, configuration, testing, and staff training. This phase ensures assets meet performance specifications and are properly integrated with existing systems. Deployment activities create baseline data for CMMS tracking and establish operational parameters.
Asset Operation and Utilization
Daily asset usage to support business operations, including performance monitoring, utilization tracking, and compliance management. This phase focuses on maximizing asset productivity while maintaining safety and regulatory standards. Operational data feeds into CMMS systems and provides insights for optimization decisions.
Asset Maintenance and Support
Systematic preservation of asset functionality through preventive maintenance, corrective repairs, and performance optimization. Activities include scheduled maintenance, condition monitoring, spare parts management, and technical support. CMMS platforms coordinate maintenance workflows while IoT sensors provide real-time asset health data.
Asset Performance Optimization
Continuous analysis and improvement of asset performance through data analytics, process refinement, and technology upgrades. This phase identifies opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and extend asset lifespan through predictive maintenance and optimization strategies.
Asset Retirement and Disposal
Structured decommissioning of end-of-life assets, including data migration, environmental compliance, asset disposal, and replacement planning. Retirement activities coordinate across ERP financial systems and CMMS maintenance records to ensure proper documentation and regulatory compliance.
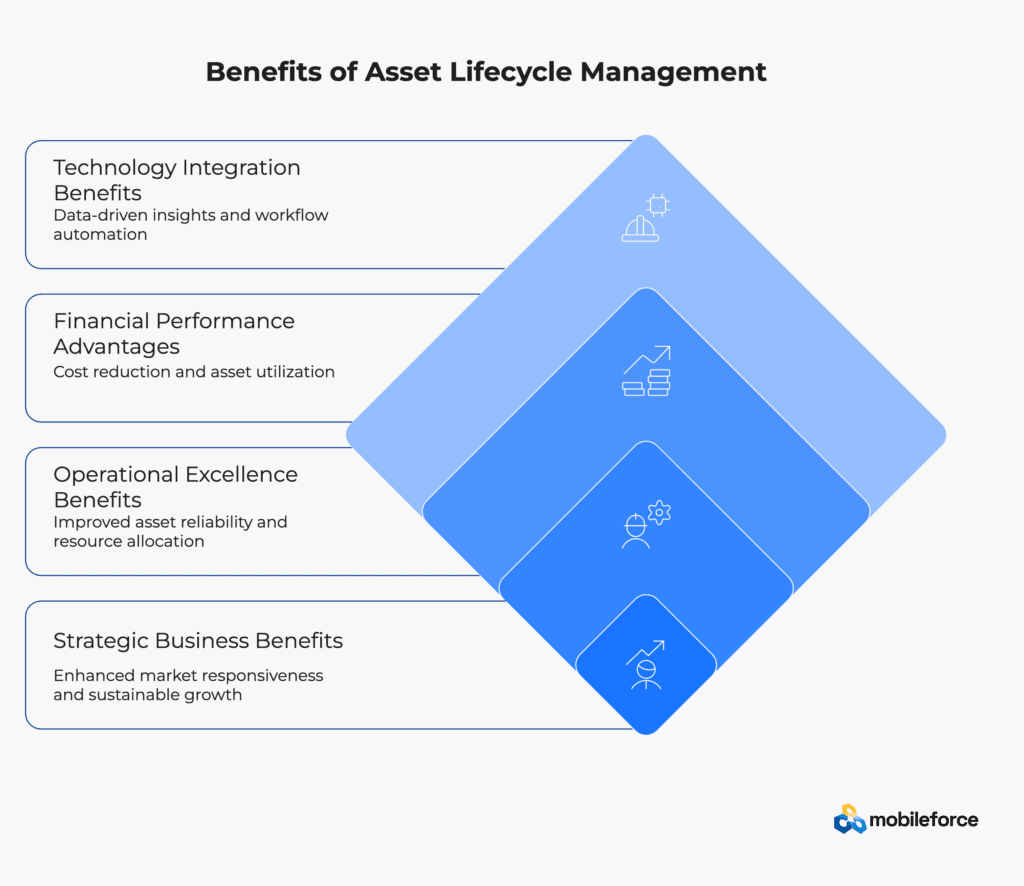
Key Benefits of Asset Lifecycle Management
Financial Performance Advantages
Organizations implementing comprehensive ALM frameworks typically achieve 20-35% reductions in total cost of ownership and 15-25% improvements in asset utilization rates. This systematic approach transforms asset management from a cost center into a strategic value driver that directly impacts profitability and competitive positioning.
Capital Investment Optimization
ALM enables data-driven asset investment decisions that maximize return on investment while minimizing unnecessary capital expenditure. Companies report 25-40% improvements in asset procurement efficiency as standardized evaluation processes eliminate emotional decision-making and ensure optimal vendor selection.
Operational Cost Reduction
Strategic maintenance planning and predictive analytics reduce unplanned downtime by up to 70%, while optimized maintenance schedules decrease overall maintenance costs by 20-30%. This approach shifts organizations from reactive firefighting to proactive asset stewardship.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance
ALM frameworks provide built-in compliance monitoring and risk management protocols that protect organizations from regulatory violations and safety incidents. Comprehensive asset documentation and maintenance records support audit requirements and insurance claims while reducing liability exposure.
Operational Excellence Benefits
Enhanced Asset Reliability
Predictive maintenance and condition monitoring increase asset availability and reduce unexpected failures. Organizations experience 30-50% improvements in equipment uptime as proactive interventions prevent costly breakdowns and production disruptions.
Improved Resource Allocation
Real-time asset performance data enables optimal resource deployment and maintenance scheduling. Teams work more efficiently when asset conditions are continuously monitored, and maintenance activities are prioritized based on actual need rather than arbitrary schedules.
Streamlined Decision Making
Integrated dashboards and analytics provide managers with actionable insights for strategic planning and operational adjustments. Asset leaders can identify trends, predict replacement needs, and make evidence-based decisions that optimize both performance and costs.
Strategic Business Benefits
Competitive Advantage
Organizations with mature ALM practices respond faster to market opportunities because their assets are more reliable and flexible. This operational excellence translates into improved customer service, faster product delivery, and enhanced market responsiveness.
Sustainable Growth Framework
As organizations expand operations or acquire new facilities, ALM provides proven methodologies for asset integration and optimization. New assets can be deployed faster and with greater confidence because established frameworks guide implementation and management processes.
Innovation Enablement
Well-managed assets provide stable foundations for business innovation and process improvement. When equipment operates reliably, organizations can focus resources on growth initiatives rather than crisis management and emergency repairs.
Technology Integration Benefits
Data-Driven Insights
Modern ALM platforms combine IoT sensors, predictive analytics, and machine learning to provide unprecedented visibility into asset performance and health. These capabilities enable proactive maintenance decisions and optimize asset lifecycle timing.
Integrated Workflow Automation
Seamless connectivity between ALM, ERP, and CMMS systems eliminates manual data entry and ensures consistent information across all business functions. This integration reduces errors while providing complete visibility into asset financial and operational performance.
Mobile Workforce Empowerment
Field technicians access real-time asset information, maintenance histories, and diagnostic tools through mobile applications. This capability improves maintenance quality and efficiency while reducing equipment downtime and repair costs.
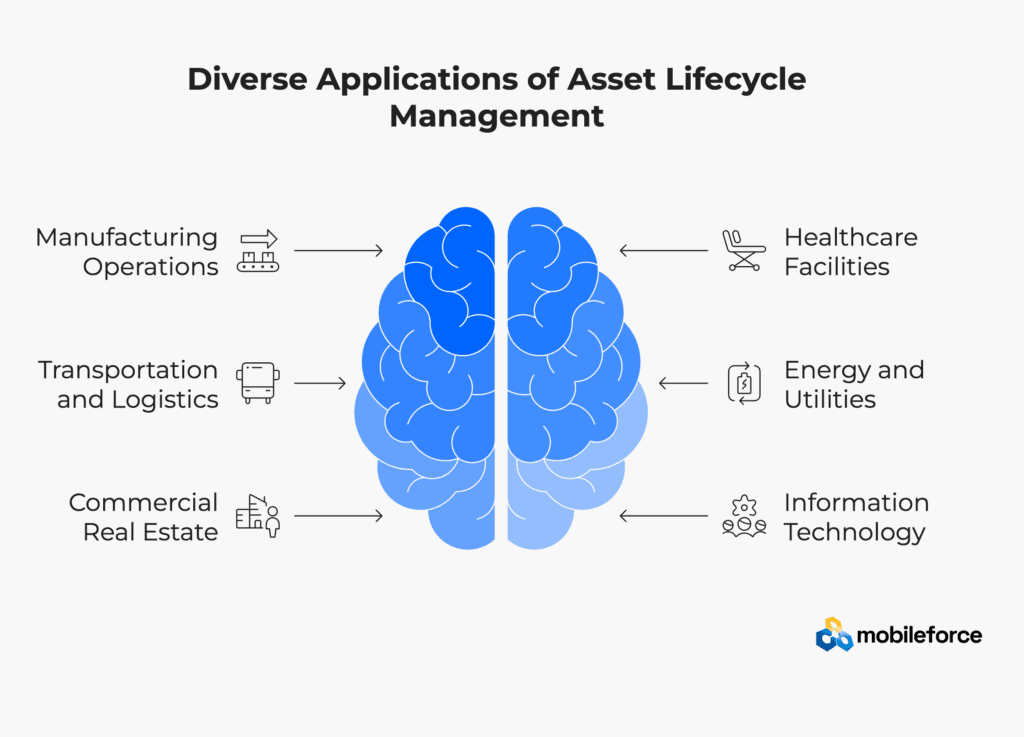
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Manufacturing Operations
Implementing ALM to optimize production equipment lifecycle management, from initial capital planning and equipment procurement through predictive maintenance programs and strategic replacement timing. Integration with ERP systems ensures accurate financial tracking while CMMS platforms coordinate maintenance activities.
Healthcare Facilities
Applying ALM frameworks to medical equipment and facility infrastructure management, encompassing regulatory compliance tracking, preventive maintenance scheduling, and lifecycle cost optimization. Specialized ALM approaches address unique healthcare requirements for equipment validation and patient safety protocols.
Transportation and Logistics
Utilizing ALM to manage vehicle fleets, material handling equipment, and infrastructure assets throughout their operational lifecycle. Real-time tracking and predictive maintenance capabilities optimize asset utilization while reducing operational costs and safety risks.
Energy and Utilities
Deploying comprehensive ALM for power generation equipment, transmission infrastructure, and distribution systems. Advanced analytics and condition monitoring enable predictive maintenance strategies that maximize asset reliability while ensuring regulatory compliance and grid stability.
Commercial Real Estate
Implementing ALM methodologies for building systems, HVAC equipment, and facility infrastructure management. Integrated approaches optimize tenant satisfaction while minimizing operational costs through strategic maintenance planning and energy efficiency initiatives.
Information Technology
Applying ALM principles to IT infrastructure, including servers, networking equipment, and software licensing management. Lifecycle optimization strategies balance performance requirements with budget constraints while ensuring security and compliance standards.
Implementation Considerations
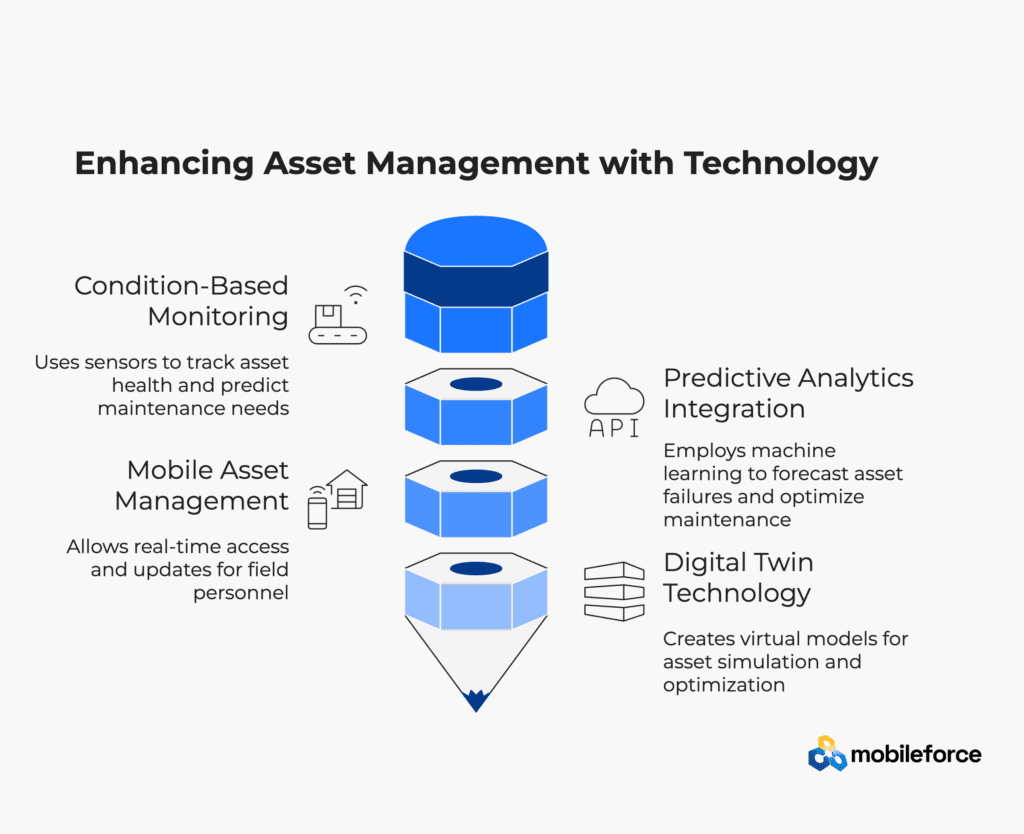
Condition-Based Monitoring
Advanced sensor technologies that continuously track asset health parameters such as vibration, temperature, pressure, and electrical characteristics. Condition-based monitoring enables predictive maintenance decisions based on actual asset condition rather than predetermined schedules.
Predictive Analytics Integration
Machine learning algorithms that analyze historical performance data, operating conditions, and maintenance records to predict asset failures and optimize maintenance timing. Predictive analytics transforms maintenance from reactive to proactive, reducing costs and improving reliability.
Mobile Asset Management
Real-time applications enabling field personnel to access asset information, update maintenance records, capture inspection data, and communicate with operations from any location. Mobile capabilities ensure data accuracy while improving maintenance efficiency and response times.
Digital Twin Technology
Virtual representations of physical assets that combine real-time sensor data with engineering models to simulate asset behavior and predict performance outcomes. Digital twins enable advanced scenario planning and optimization strategies for complex assets.
Key Performance Indicators
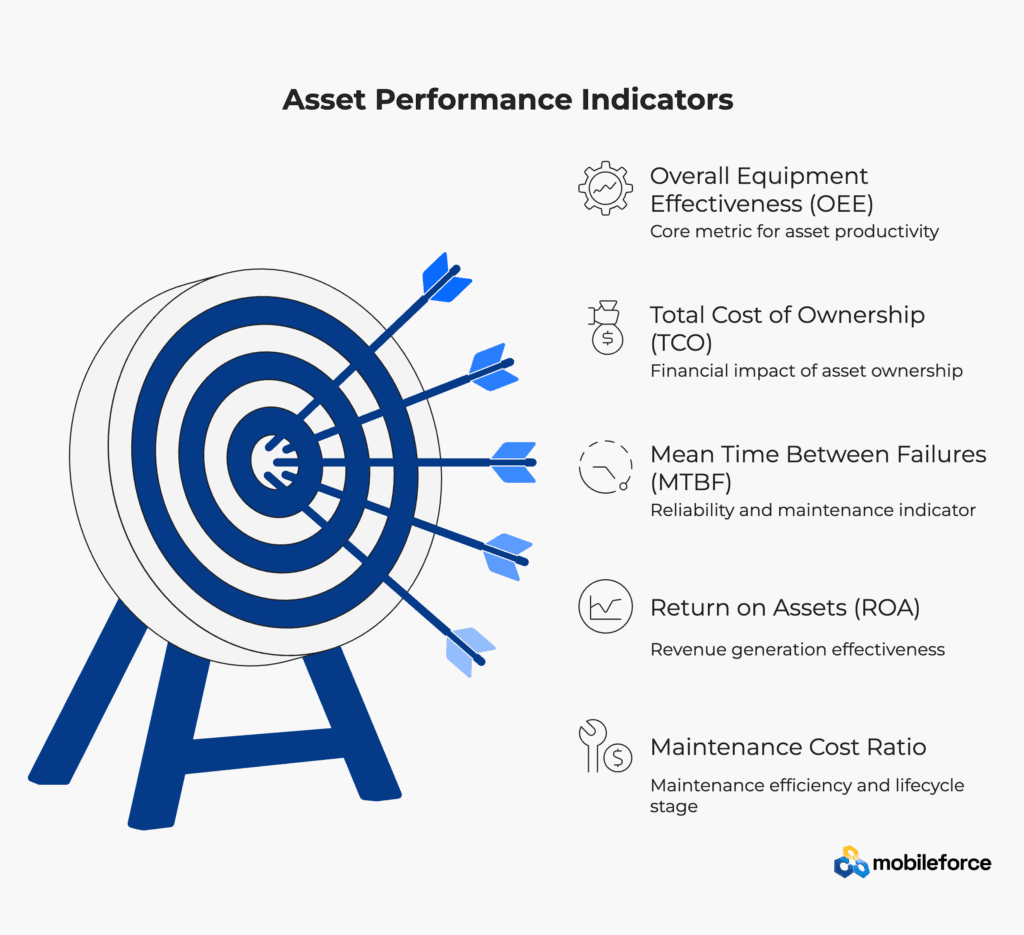
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
A comprehensive metric measuring asset productivity by combining availability, performance efficiency, and quality rates. OEE provides a single indicator of how effectively assets are utilized and identifies opportunities for improvement.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The complete financial impact of asset ownership, including acquisition costs, operating expenses, maintenance costs, and disposal values. TCO analysis supports optimal asset selection and lifecycle timing decisions.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
The average operational time between asset failures or significant maintenance events. MTBF indicates asset reliability and helps predict maintenance requirements and spare parts needs.
Return on Assets (ROA)
A financial metric measuring how effectively assets generate revenue relative to their book value. ROA demonstrates asset management effectiveness and guides investment allocation decisions.
Asset Utilization Rate
The percentage of time assets are productively employed versus their total available time. Utilization rates identify underperforming assets and opportunities for capacity optimization.
Maintenance Cost Ratio
The proportion of maintenance expenses relative to asset replacement value, providing insights into maintenance efficiency and asset lifecycle stage. This metric helps optimize maintenance spending and replacement timing.
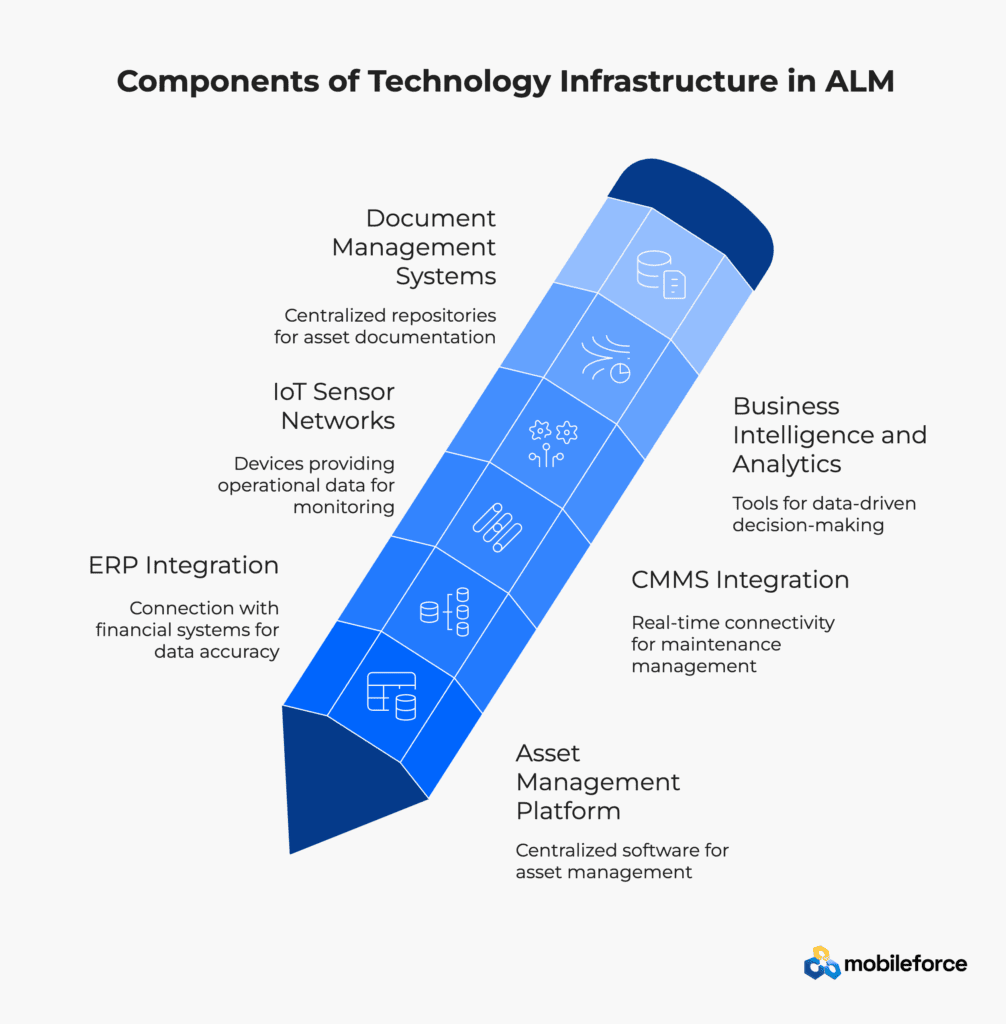
Technology Infrastructure
Asset Management Platform
Integrated software centralizing asset registries, maintenance schedules, performance tracking, and lifecycle analytics with workflow automation and reporting capabilities. Modern platforms provide APIs for seamless integration with ERP systems for financial data and CMMS platforms for operational execution.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Integration
Connection between ALM and financial systems that ensures asset investments, depreciation schedules, and maintenance costs are accurately captured and reported for financial planning and analysis. ERP integration provides complete visibility into asset financial performance.
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) Integration
Real-time connectivity between ALM frameworks and maintenance management platforms that enables automated work order generation, resource scheduling, and maintenance history tracking based on asset conditions and lifecycle requirements.
Internet of Things (IoT) Sensor Networks
Connected devices providing continuous operational data for condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated alert generation. IoT data feeds into ALM analytics engines and CMMS scheduling systems to enable proactive asset management.
Business Intelligence and Analytics
Advanced reporting and visualization tools that transform asset data into actionable insights for strategic decision-making. Analytics platforms identify trends, predict failures, and optimize asset lifecycle timing through data-driven recommendations.
Document Management Systems
Centralized repositories for asset documentation, including specifications, warranties, maintenance procedures, and compliance records. Document management ensures critical information is accessible throughout the asset lifecycle while supporting audit and regulatory requirements.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Environmental Compliance
Management of environmental regulations affecting asset operation and disposal, including emissions monitoring, waste management, and sustainability reporting requirements. ALM frameworks ensure environmental compliance throughout asset lifecycles.
Safety and Health Standards
Integration of occupational safety requirements into asset management processes, including equipment certification, safety training, and incident tracking. Safety compliance protects workers while reducing liability and regulatory risks.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Specialized compliance requirements for regulated industries such as healthcare, aviation, nuclear, and pharmaceuticals. ALM systems accommodate unique regulatory frameworks while maintaining operational efficiency.
Data Security and Privacy
Protection of asset data and operational information through cybersecurity measures, access controls, and privacy protocols. Security frameworks safeguard critical infrastructure while enabling authorized access to asset information.
Conclusion
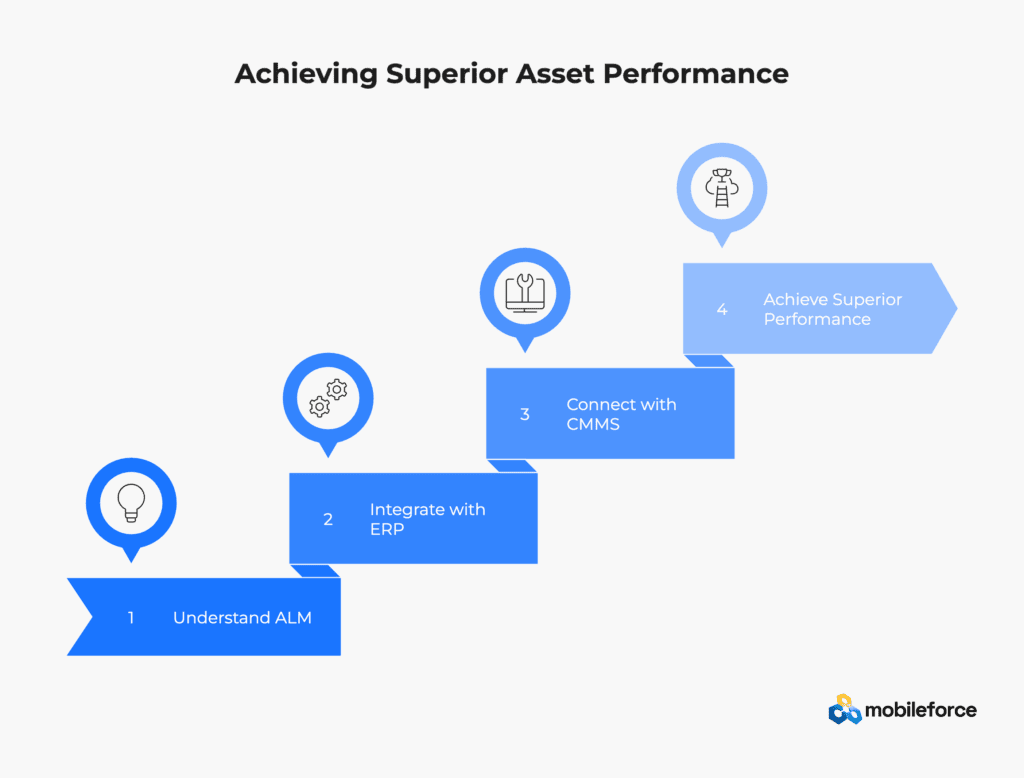
Understanding Asset Lifecycle Management terminology is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their physical and digital asset investments. Modern ALM implementations integrate seamlessly with ERP systems for comprehensive financial tracking while connecting with CMMS platforms for efficient maintenance execution and operational excellence.
For organizations evaluating comprehensive asset management solutions, these ALM principles provide the foundation for creating integrated workflows that span from initial asset planning through strategic disposal. The right technology ecosystem combines ALM frameworks with ERP financial accuracy and CMMS operational capabilities, positioning organizations to achieve superior asset performance, reduced total cost of ownership, and sustainable competitive advantages through strategic asset stewardship.